December 11.2025

The Elo D2 Damac project in Motor City, Dubai, represents a fusion of modern architecture, lifestyle-driven design, and strategic digital execution. Spanning 536,000 ft² across two 14-storey residential towers, this development offers 1- and 2-bedroom apartments surrounded by resort-style amenities, landscaped gardens, and direct connectivity to central Dubai via Al Qudra Road.
To support quantity take-offs and modelling during the award phase, the project team adopted Glodon Cubicost TAS and TRB. This decision strengthened efficiency, improved accuracy, and ensured confidence in the project’s delivery. Set for completion in 2028, Elo D2 Damac showcases how digital tools and strong industry partnerships can elevate residential construction standards in the Middle East.
About the Elo D2 Damac Project and Land Sterling
Elo D2 Damac is designed as a vibrant residential community within Dubai’s growing suburban landscape, combining modern living spaces with urban convenience. With its integration of detailed architectural elements, repeated structural components, and varied façade features, the project required a highly precise and adaptable digital approach.
Land Sterling, established in Dubai in 2009, is a leading RICS-regulated real estate consultancy known for its valuation, cost consultancy, and project advisory services. With extensive experience across the UAE, the firm applies global best practices and deep regional expertise. For this project, Quantity Surveyor Eldvin led the adoption of Cubicost TAS and TRB to ensure accurate quantification and a streamlined workflow.
Challenges in Measurement and Modelling
The Elo D2 Damac development presented several technical and workflow challenges for the QS team, especially during the tender and award stage.
1. Navigating PDF Drawings Without Layers
Working from non-layered PDF drawings made it difficult to identify, classify, and extract quantities efficiently. Manual intervention was required to interpret design intent, slowing down take-off preparation.
2. Complex Architectural Elements
Façades and intricate architectural components required careful handling, adding complexity during modelling and increasing the risk of inaccuracies without advanced digital tools.
3. Repetitive Components Across Floors
Elements that repeated floor by floor significantly increased modelling workload. Duplicating detailed items manually posed a high risk of inconsistency and required additional time for quality checks.
4. Tight Time Constraints in Pre-Contract Stage
The awarded stage required quantity take-offs to be completed quickly and accurately. Balancing speed with precision created pressure during reporting and verification.
Transformation with Glodon Cubicost TAS and TRB
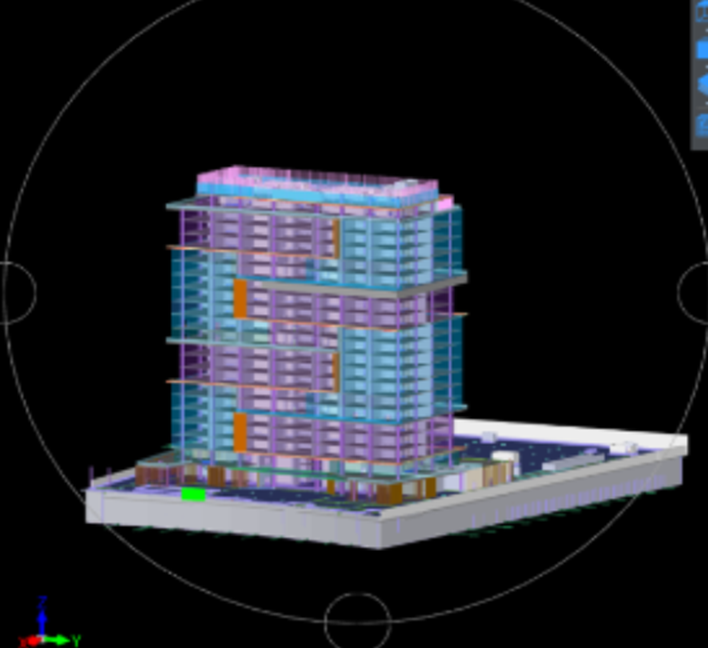
Figure 1. Cubicost TAS: Complete Measurement of Architectural and Structural Elements
To overcome these challenges, the project team employed several key Cubicost features and workflow strategies that elevated accuracy and efficiency.
1. Faster Modelling with Copy-Paste and Floor Replication
Manual modelling was enhanced using copy-paste functions and Copy to Other Floor to reduce repetitive work and maintain consistency in typical floor layouts.
2. Custom Elements and Quantity Functions for Complex Architecture
Custom elements and specialised quantity functions enabled the accurate modelling of complex façades and non-standard objects. Tools like the Vector Graphics Editor improved versatility and precision.
3. 3D Visualisation and View Expression for Verification
3D modelling tools and view expressions were extensively used to detect inconsistencies, verify quantities, and reduce errors before final reporting, ensuring smoother coordination with stakeholders.
4. Create Legend for Clear Visual Communication
The Create Legend function enabled drawings, modelled elements, and quantities to be displayed clearly on a single page, making it easier to communicate take-off results through structured PDF outputs.
5. Reusable Component Libraries for Consistent Modelling
Reusable element libraries were developed by exporting Cubic files. These libraries enabled fast application of frequently used elements and ensured consistent modelling across the entire project and future works.
Results and Benefits Achieved
The integration of Cubicost TAS and TRB delivered several noteworthy advantages, directly addressing project complexities and supporting high-quality outcomes.
1. High-Precision Modelling
Complex façades and irregular building features were modelled with accuracy, enabling dependable quantity take-offs even from PDF drawings.
2. Significant Time Efficiency
Reusable component libraries and automated modelling, such as ramp creation, reduced modelling time and supported timely delivery during demanding pre-contract phases.
3. Improved Communication Across Stakeholders
3D views, view expressions, and clear 2D mark-ups made quantities easier to understand and validate, reducing misinterpretations and supporting smoother discussions.
4. Structured and Standardised Workflow
By reducing repetitive work and ensuring consistent modelling practices, productivity improved, enabling the team to complete modelling and QTO stages with clarity and control.
5. Timely and Accurate Project Delivery
The workflows and Cubicost tools ensured that quantity take-offs and models were completed on schedule, supporting timely approvals and strong project progression.
The Elo D2 Damac development in Dubai highlights how Glodon Cubicost TAS and TRB can transform tender-stage precision, streamline modelling, and support confident decision-making for residential projects. By adopting structured modelling practices and digital tools, Land Sterling demonstrated how accuracy, speed, and clarity can redefine project outcomes in the Middle East.
Ready to reduce errors, speed up take-offs, and streamline your project delivery? Glodon Cubicost equips your team with the tools needed for accurate, efficient, and transparent construction workflows.
Speak with us today through our Contact Us page to get started.



